这一段代码在你眼里看来是代码,但是在gcc看来,就是一串可能包含代码的字符串,经过处理之后,我们需要把这段代码解析成下面正确的汇编代码,从而经过之后的链接器等完成最终可执行文件的生成操作,而读入代码,生成汇编文件 这个过程就涉及到了有限自动机(FAM) 这个模型,它将一个系统分成若干可数个离散的状态,在识别到特定模式后,进行对应的跳转,最终再进行判断。
.file"a.c".text .section .rodata.str1.1,"aMS",@progbits,1 .LC0: .string"%d".LC1: .string"%d\n".text .globl main .type main, @function main: .LFB11: .cfi_startproc subq $24, %rsp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 32 movl $0, 12(%rsp) leaq 12(%rsp), %rsi movl $.LC0, %edi movl $0, %eax call __isoc99_scanf movl 12(%rsp), %eax leal 10(%rax), %esi movl $.LC1, %edi movl $0, %eax call printf movl $0, %eax addq $24, %rsp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 8 ret .cfi_endproc .LFE11: .size main, .-main .ident"GCC: (GNU) 13.2.0".section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits 而字符串的操作还远不止这些,关于有限自动机以及编译器的实现细节等内容,你将会在未来的编译原理课程中学到(当然是你们学校开的课,我还没有写编译原理博客的计划),在这一篇当中,我们会介绍字符串的ADT,基本操作,以及两种常用的字符串模式匹配算法 。
(1).字符串及其ADT #1.基本概念 vc; for (int i = beg; i <= end; i++) { vc.push_back(container[i]); } return string{ vc }; } 还有一种子串的取法则是从位置i开始取j个字符形成子串,这个实现方法其实没什么太大的区别,你可以自己尝试实现。
#2.插入字符串insert 这个函数其实和线性表向其中某个位置插入指定个数的元素的操作差不多,所以我们也可以很快地写出下面的代码:
string insert(const string& s1, int pos) { if (pos > _size) pos = _size; else if (pos < 0) pos = 0; container.resize(_size + s1.size() + 100); // 给容器直接扩容,避免之后再挪动的时候出现越界访问的问题 int mov = s1.size(); for (int i = _size-1; i >= pos; i--) { container[i + mov] = container[i]; } for (int i = pos; i < mov; i++) { container[i] = s1.container[i - pos]; } return *this; } #3.其他操作 其他操作真的很简单,比如concat,如果操作的是vector,一个个push_back就好了,这些操作还是自己实现一下吧。
(3).字符串的模式匹配 什么是模式匹配呢,听起来有点复杂,不过其实很简单,就是依照查找子串 的事情,比如:在hellowbabababbabbba中找到babb
#1.简单匹配(Brute-Force方法)怎么找呢?很自然的想法就是一个个去遍历,比如这样:
int find_bf(const string& t, const string& p, int pos) { int i{ pos }, j{ 0 }; int n = t.size(), m = p.size(); while (i < n && j < m) { if (t[i] == p[i]) { i++, j++; } else { i += 1-j; j = 0; } } if (j == m) return i - m; else return -1; } 很简单,每到一个字符就往后匹配一次,匹配不上就继续遍历,如果匹配上了就直接返回,这样就好了
假设正文字符串长度为n ,模式字符串长度为m ,那么这个匹配方式的时间复杂度是 O ( n m ) O(nm) O(nm),如果模式串和正文串长度差不多,这个匹配方式的时间复杂度就会退化到 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)的时间复杂度,这有点太慢了。
#2.KMP算法 Knuth,Morris和Pratt共同提出了一种全新的模式匹配算法,这个算法能够在 O ( n + m ) O(n+m) O(n+m)的线性时间复杂度内完成字符串的模式匹配。
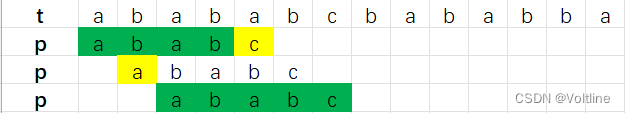
我们先来思考一下,Brute-Force方法到底有什么问题,比如t = abababcbababba,p = ababc,BF方法是这样:
我们会发现,p和t在第一次匹配的时候,前面的abab都已经匹配上了,只有c和a发生了失配 ,而因为失配,第二次我们把整个字符串往后挪动一次匹配,还得从a开始,这样我们貌似忘记了前面四个字符是匹配 的了
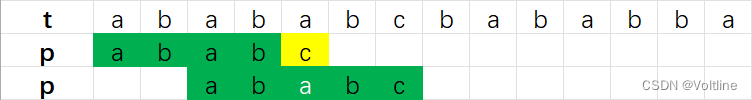
如果我们试着看看t可能可以发现这么一件事,出现的第二个ab后面又是a,而在字符串p中,第一个ab后出现的也是a,所以如果我们的p可以这么跳转:
只让p对应的那个指针 动,动到刚才我们发现的"aba"的地方,就可以去掉第二次匹配,这个例子举的可能差距不大,我们把t变成abababababcbab,那么情况就会变成这样:
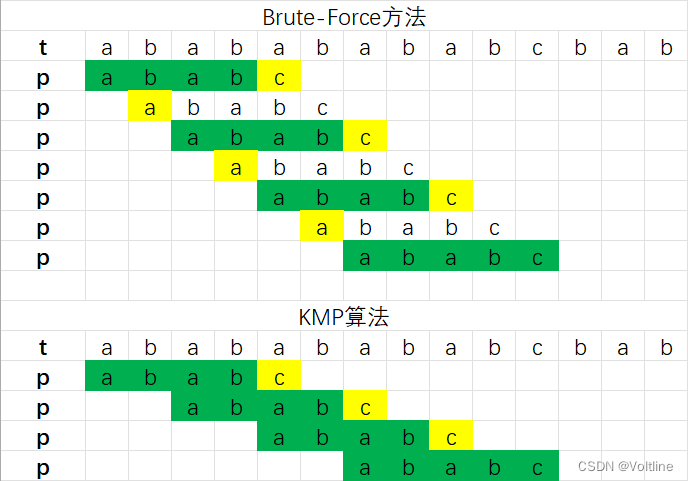
比较次数明显减少!所以KMP算法的核心就在于:如何找到模式字符串本身具备的特性,通过它本身的性质得到一个失配跳转值,从而尽可能增加每一次模式字符串跳转的字符数,从而大大减少重复匹配的次数 ,接下来我们来具体提一提怎么实现KMP算法
I.kmp_match() 这次我打算先介绍一下,我们如何通过这个想法进行匹配,假设我们已经获得了对于模式字符串的next数组(这个等会儿再来看怎么实现),接下来要对正文串t和模式串p进行匹配,那么基于前面我们说的想法:在匹配的时候就继续前进,失配的时候根据失配跳转值让p向前跳 ,如果到第一个字符还是失配,那就不可能在现在已经走过的字符里找到能匹配的了 ,这时候只要让t的指针往后跳一个就行了,所以我们可以得出下面的代码:
struct chars { char c; // 字符 int idx; // 跳转值 }; int kmp(const string& t, const string& p) { int ans{ -1 }; vector next = getNext(p); int t_size = t.size(), p_size = p.size(); int i{ 0 }, j{ 0 }; while (i < t_size) { if (j == -1 || t[i] == p[j]) { i++, j++; } else { if (j < p_size) j = next[j].idx; } if (j == p_size) { ans = i - j; break; } } return ans; } 我们首先用getNext()函数获得next数组,然后进行基于next数组的匹配,next数组的数据模式如下:第一个字符对应的值为-1,其他的字符对应的值则是对应字符失配时的跳转值 ,如果找到的next值是-1,就让指向正文串的"指针"i向后移动一位,否则就让指向模式串的"指针"j移动到next[j]的位置上去。
那么接下来,我们就来看看这个getNext()函数怎么写的吧!
II.getNext() 首先说一说前缀 和后缀 的概念,前缀就是自第一个字符起的所有连续子串 ,后缀就是自最后一个字符起的所有连续子串 ,提到前缀和后缀主要是为了引入next的计算原理。
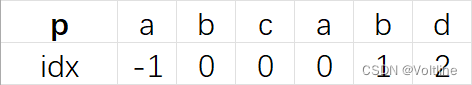
接下来我们来看看next数组是怎么生成的,next数组的跳转顺序基于这样一个规则:当失配发生时,失配字符a的上一个字符b对应的某一个子串S在不包含当前子串的最长前缀中,子串S最后一次出现的位置中,字符b的位置 ,有点拗口,我们来详细地解释一下,例如:p = abcabd,我们找next的规则就是基于每个下一个字符都有可能是失配字符来做的 ,那么我们可以得到下面的一张表:
a首先是-1没问题,b去往前找,只有a,那就赋为0吧。之后是c,往前找一个字符是b,它对应的idx是0,next[0]是a,a和b并不匹配,那就继续往前走,字符a对应的idx是-1,这时候就结束了,我们让c的idx为a的idx+1,也就是0。
然后又是b,b前面一个字符是a,而a在前面的字符中出现过,在第0个,因此当这个b失配的时候,下一次我们可以试着从它前面一个字符出现的上一次的后面一个字符继续匹配 ,很显然,a在0出现了,后面一位是1,所以b就赋为1了。
最后是d,d前面一个字符是b,而b上一次出现在数组中是1,那么d失配的时候,b满足,就跳转到上一次出现的b的后面一位,也就是c,对应的是2 ,所以d就赋为2了。
然后我们就走完了全程,你发现了,虽然我们是在做子串和前缀的重叠匹配 ,但是实际上,因为每个字符的上一个字符总是已经包含了之前字符的重叠情况 ,因此我们只需要考虑当前这个字符是不是匹配就好了,这其实也能算是一种动态规划 的思想,因为我们让每一次字符的查找都变得有用了起来,每一次下一个字符的查找都基于上一个查找的结果来确定,因此查找的过程就变得简单了起来:
1.到了某一个字符c,先看看这个字符的前一个字符 2.如果这个字符的前一个字符b和b自己的next值对应的字符相同,那就让c的next值等于b的next值+1(允许你从上一次b出现的后面一个字符开始匹配) 3.如果这个字符的前一个字符b和b自己的next值对应的字符不相同,那就让继续找到b的next值对应的字符对应的next值,继续往前找,直到找到一个匹配的字符,或者找到第一个字符(对应的next值为-1),如果找到匹配的字符,则类似2操作,让c的next值等于找到的这个字符的位置+1;否则就赋值为0,对应最前的字符 很好,那代码就很好写了:
vector getNext(const string& sub_str) { vector next; size_t sub_str_size{ sub_str.size() }; next.push_back(chars{ sub_str[0], -1 }); for (size_t i = 1; i < sub_str_size; i++) { next.push_back(chars{ sub_str[i], 0 }); } for (size_t i = 1; i < sub_str_size; i++) { if (next[i - 1].idx != -1 && next[i - 1].c == next[next[i - 1].idx].c) { next[i].idx = next[i - 1].idx + 1; } else { int j = next[i - 1].idx; while (j != -1 && next[j].c != next[i - 1].c) { j = next[j].idx; } next[i].idx = j + 1; } } return next; } 我这里next存的是一个叫做chars的结构体,它对应的结构是这样:
struct chars { char c; // 字符 int idx; // 跳转值 }; 其实你只存这个idx也是可以的,你可以稍微改改,有一个特别需要注意的点:
for (size_t i = 1; i < sub_str_size; i++) { next.push_back(chars{ sub_str[i], 0 }); } 这个数组在初始化的时候,我们把所有后续字符的idx值都赋为0,如果没有后续的操作,这个情况如果调用kmp_match函数的匹配过程就会和前面说的Brute-Force方式完全一样了 ,所以后续的找next过程还是非常重要的呢!那么KMP算法其实到这里基本上就结束了,我们会发现,如果真的理解了它的做法,其实感觉还挺简单的,实际上就是一个动态规划 的思想,很多动态规划的问题也是这样,其实想出来之后它的思路并不复杂,但是要想到这个思路的过程是相当困难的。
#3.还有更多 其实字符串的匹配方式还有很多很多,例如BM算法等,因为时间的限制,在这里我就不做过多介绍了。
小结 字符串这一篇,相当的短啊哈哈哈哈哈哈,毕竟这一部分在数据结构中我们主要还是以掌握KMP算法 为主,毕竟它在模式匹配上表现出的时间复杂度 O ( n + m ) O(n+m) O(n+m)是非常优秀的。下一篇我们将会介绍一系列内部排序的算法。
附录:我自己写的string #pragma once #include #include #include"vector.h"namespace MySTL { template class basic_string { private: vector container; size_t _size; public: using iterator = T*; using const_iterator = const T*; inline static size_t npos = -1; public: basic_string(); basic_string(const char* _c_str); basic_string(const char* _c_str, size_t _size); basic_string(const char* _c_str, size_t _begin, size_t _size); basic_string(size_t _size, char c); basic_string(const basic_string& _str); basic_string(basic_string&& _mv_str) noexcept; basic_string(std::initializer_list l); ~basic_string(); basic_string& operator=(const basic_string& _Right); basic_string& operator=(basic_string&& _Right) noexcept; basic_string& operator=(const char* _str); basic_string& operator=(char c); basic_string operator+(const basic_string& _Right); basic_string operator+(const char* _str); basic_string operator+(char c); basic_string& operator+=(const basic_string& _Right); basic_string& operator+=(const char* _str); basic_string& operator+=(char c); T& operator[](size_t _index); const T& operator[](size_t _index) const; T& at(size_t _index); bool operator==(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator!=(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator>(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator<(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator>=(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator<=(const basic_string& _Right); bool operator==(const char* _c_Right); bool operator!=(const char* _c_Right); bool operator>(const char* _c_Right); bool operator<(const char* _c_Right); bool operator>=(const char* _c_Right); bool operator<=(const char* _c_Right); size_t size() const noexcept; size_t capacity() const noexcept; bool empty() const noexcept; const T* data(); const T* c_str(); iterator begin(); iterator end(); const_iterator begin() const; const_iterator end() const; void reserve(size_t new_capacity_size); void resize(size_t new_elem_size); void clear(); void erase(const size_t _Where); void erase(const size_t _Off, const size_t _Count); void erase(iterator _begin, iterator _end); void erase(iterator _pos); void append(size_t _Count, char c); void append(const basic_string& _str); void append(const basic_string& _str, size_t _Begin = 0); void append(const basic_string& _str, size_t _Begin, size_t _Count); void append(const char* _str); void append(const char* _str, size_t _Begin); void append(const char* _str, size_t _Begin, size_t _Count); void append(std::initializer_list l); void push_back(char c); size_t find(char c, size_t _begin_pos = 0); size_t find(const char* _str, size_t _begin_pos = 0); size_t find(const basic_string& _str, size_t _begin_pos = 0); void swap(basic_string& _Right); template friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output, const basic_string& _str) { for (auto& i : _str) { output << i; } return output; } template friend std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& input, basic_string& _str) { _str.clear(); U c = input.get(); while (c != ' ' && c != '\n' && c != '\t') { _str.push_back(c); c = input.get(); } return input; } }; templatebasic_string::basic_string() { container = vector{}; } templatebasic_string::basic_string(const char* _c_str) { size_t length{ strlen(_c_str) }; _size = length; container = vector(); for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { container.push_back(*(_c_str + i)); } container.push_back('\0'); } templatebasic_string::basic_string(const char* _c_str, size_t _size) { size_t length{ _size }; if (_size > strlen(_c_str)) { length = strlen(_c_str); } _size = length; container = vector(); for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { container.push_back(*(_c_str + i)); } container.push_back('\0'); } templatebasic_string::basic_string(const char* _c_str, size_t _begin, size_t _size) { size_t c_str_len{ strlen(_c_str) }; container = vector(); if (_begin > c_str_len) { _size = 0; } else { size_t length{ _size }; if (_size > strlen(_c_str + _begin)) { length = strlen(_c_str + _begin); } _size = length; for (size_t i = _begin; i < length; i++) { container.push_back(*(_c_str + i)); } container.push_back('\0'); } } templatebasic_string::basic_string(size_t _size, char c) { container = vector(_size, c); _size = _size; } templatebasic_string::basic_string(const basic_string& _str) { container = vector(_str.container); _size = _str._size; } templatebasic_string::basic_string(basic_string&& _mv_str) noexcept { container = std::move(_mv_str.container); _size = _mv_str._size; _mv_str.container = vector{}; } templatebasic_string::basic_string(std::initializer_list l) { container = vector(l.size() + 128); _size = l.size(); for (auto it = l.begin(); it != l.end(); it++) { container.push_back(static_cast(*it)); } container.push_back('\0'); } templatebasic_string::~basic_string() { _size = 0; container.~vector(); } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator=(const basic_string& _Right) { container.~vector(); container = _Right.container; _size = _Right._size; return *this; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator=(basic_string&& _Right) noexcept { container.~vector(); container = std::move(_Right.container); _size = _Right._size; return *this; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator=(const char* _str) { container.~vector(); size_t length{ strlen(_str) }; container = vector(length + 128); _size = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { container.push_back(_str[i]); _size++; } return *this; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator=(char c) { clear(); push_back(c); return *this; } templatebasic_stringbasic_string::operator+(const basic_string& _Right) { basic_string temp{ *this }; for (auto& i : _Right) { temp.push_back(i); } return temp; } templatebasic_stringbasic_string::operator+(const char* _str) { basic_string temp{ *this }; size_t length{ strlen(_str) }; for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { temp.push_back(_str[i]); } return temp; } templatebasic_stringbasic_string::operator+(char c) { basic_string temp{ *this }; temp.push_back(c); return temp; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator+=(const basic_string& _Right) { for (auto& i : _Right) { push_back(i); } return *this; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator+=(const char* _str) { size_t length{ strlen(_str) }; for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) { push_back(_str[i]); } return *this; } templatebasic_string& basic_string::operator+=(char c) { push_back(c); return *this; } template T& basic_string::operator[](size_t _index) { return container[_index]; } template const T& basic_string::operator[](size_t _index) const { return container[_index]; } template T& basic_string::at(size_t _index) { if (_index <= _size) { return container[_index]; } else { throw std::out_of_range("Index Out of Range"); } } template bool basic_string::operator==(const basic_string& _Right) { if (_size != _Right._size) { return false; } else { for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++) { if (container[i] != _Right[i]) return false; } return true; } } template bool basic_string::operator!=(const basic_string& _Right) { return !(*this == _Right); } template bool basic_string::operator>(const basic_string& _Right) { size_t min_size{ _size < _Right.size() ? _size : _Right.size() }; for (size_t i = 0; i < min_size; i++) { if (container[i] > _Right[i]) return true; else if (container[i] < _Right[i]) { return false; } } return _size > _Right.size(); } template bool basic_string::operator<(const basic_string& _Right) { return (*this <= _Right) && (*this != _Right); } template bool basic_string::operator>=(const basic_string& _Right) { return (*this > _Right) || (*this == _Right); } template bool basic_string::operator<=(const basic_string& _Right) { return !(*this > _Right); } template bool basic_string::operator==(const char* _c_Right) { if (strlen(_c_Right) != _size) return false; else { for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; i++) { if (container[i] != _c_Right[i]) return false; } return true; } } template bool basic_string::operator!=(const char* _c_Right) { return !(*this == _c_Right); } template bool basic_string::operator>(const char* _c_Right) { size_t length{ strlen(_c_Right) }; size_t min_size{ _size < length ? _size : length }; for (size_t i = 0; i < min_size; i++) { if (container[i] > _c_Right[i]) return true; else if (container[i] < _c_Right[i]) { return false; } } return _size > length; } template bool basic_string::operator<(const char* _c_Right) { return (*this <= _c_Right) && (*this != _c_Right); } template bool basic_string::operator>=(const char* _c_Right) { return (*this > _c_Right) || (*this == _c_Right); } template bool basic_string::operator<=(const char* _c_Right) { return !(*this > _c_Right); } template size_t basic_string::size() const noexcept { return _size; } template size_t basic_string::capacity() const noexcept { return container.capacity(); } template bool basic_string::empty() const noexcept { if (_size != 0) return false; else return true; } template const T* basic_string::data() { return container.data(); } template const T* basic_string::c_str() { return container.data(); } template typename basic_string::iterator basic_string::begin() { return container.begin(); } template typename basic_string::iterator basic_string::end() { return container.begin() + _size; } template typename basic_string::const_iterator basic_string::begin() const { return container.begin(); } template typename basic_string::const_iterator basic_string::end() const { return container.begin() + _size; } template void basic_string::reserve(size_t new_capacity_size) { container.reserve(new_capacity_size); } template void basic_string::resize(size_t new_elem_size) { container.resize(new_elem_size); _size = new_elem_size; } template void basic_string::clear() { _size = 0; container.clear(); } template void basic_string::erase(const size_t _Where) { if (_Where <= _size) { _size = _Where; container.erase(container.begin() + _Where, container.end()); container.push_back('\0'); } } template void basic_string::erase(const size_t _Off, const size_t _Count) { if (_Off <= _size) { if (_size - _Off > _Count) { _size -= _Count; container.erase(container.begin() + _Off, container.begin() + _Off + _Count); container[_size] = '\0'; } else { erase(_Off); } } } template void basic_string::erase(basic_string::iterator _begin, basic_string::iterator _end) { if (_end >= _begin) { if (_begin >= begin()) { size_t _Off = _begin - begin(); size_t _Count = _end - _begin; if (_Off <= _size) { if (_size - _Off > _Count) { _size -= _Count; container.erase(container.begin() + _Off, container.begin() + _Off + _Count); container[_size] = '\0'; } else { erase(_Off); } } } else { throw IteratorOutOfRangeException{}; } } else { throw IteratorErrorException{}; } } template void basic_string::erase(basic_string::iterator _pos) { if (_pos >= begin()) { if (_pos < end()) { size_t _Where = _pos - begin(); if (_Where <= _size) { _size--; container.erase(_pos, _pos + 1); container[_size] = '\0'; } } } else { throw IteratorErrorException{}; } } template void basic_string::append(size_t _Count, char c) { for (size_t i = 0; i < _Count; i++) { push_back(c); } } template void basic_string::append(const basic_string& _str) { *this += _str; } template void basic_string::append(const basic_string& _str, size_t _Begin) { if (_Begin <= _str.size()) { if (_Begin == 0) { *this += _str; } else { for (auto it = _str.begin() + _Begin; it != _str.end(); it++) { push_back(*it); } } } else { throw std::out_of_range("Begin index out of range!"); } } template void basic_string::append(const basic_string& _str, size_t _Begin, size_t _Count) { if (_Begin <= _str.size()) { if (_Begin + _Count > _str.size()) { _Count = _str.size() - _Begin; } for (size_t i = 0; i < _Count; i++) { push_back(_str[_Begin + i]); } } else { throw std::out_of_range("Begin index out of range!"); } } template void basic_string::append(const char* _str) { *this += _str; } template void basic_string::append(const char* _str, size_t _Begin) { if (_Begin <= strlen(_str)) { *this += (_str + _Begin); } else { throw std::out_of_range("Begin index out of range!"); } } template void basic_string::append(const char* _str, size_t _Begin, size_t _Count) { if (_Begin <= strlen(_str)) { if (strlen(_str) - _Begin < _Count) { _Count = strlen(_str) - _Begin; } if (_Count != 0) { for (size_t i = 0; i < _Count; i++) { push_back(_str[_Begin + i]); } } } else { throw std::out_of_range("Begin index out of range!"); } } template void basic_string::append(std::initializer_list l) { for (auto& i : l) { push_back(i); } } template void basic_string::push_back(char c) { if (_size == container.size()) { container.push_back(c); } else { container[_size] = c; } container.push_back('\0'); _size++; } template size_t basic_string::find(char c, size_t _begin_pos) { for (size_t i = _begin_pos; i < _size; i++) { if (container[i] == c) { return i; } } return npos; } template size_t basic_string::find(const char* _str, size_t _begin_pos) { size_t length{ strlen(_str) }; bool isFind{ true }; if (_size < length) return npos; else { for (size_t i = _begin_pos; i < _size; i++) { if (_size - i >= length) { if (container[i] == _str[0]) { isFind = true; for (size_t j = 1; j < length; j++) { if (container[i + j] != _str[j]) { i = i + j - 1; isFind = false; break; } } if (isFind) return i; } } else { return npos; } } return npos; } } template size_t basic_string::find(const basic_string& _str, size_t _begin_pos) { size_t length{ _str.size() }; bool isFind{ true }; if (_size < length) return npos; else { for (size_t i = _begin_pos; i < _size; i++) { if (_size - i >= length) { if (container[i] == _str[0]) { isFind = true; for (size_t j = 1; j < length; j++) { if (container[i + j] != _str[j]) { i = i + j - 1; isFind = false; break; } } if (isFind) return i; } } else { return npos; } } return npos; } } template void basic_string::swap(basic_string& _Right) { basic_string temp{ _Right }; _Right.clear(); for (auto& c : *this) { _Right.push_back(c); } clear(); for (auto& c : temp) { push_back(c); } } template bool operator==(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right == _Left; } template bool operator!=(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right != _Left; } template bool operator>(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right < _Left; } template bool operator<(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right > _Left; } template bool operator>=(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right <= _Left; } template bool operator<=(const char* _Left, const basic_string& _Right) { return _Right >= _Left; } template std::istream& getline(std::istream& input, basic_string& _Target, const char _End = '\n') { _Target.clear(); T c = input.get(); while (c != '\n') { _Target.push_back(c); c = input.get(); } return input; } using string = basic_string; using wstring = basic_string; #ifdef __cpp_lib_char8_t using u8string = basic_string; #endif // __cpp_lib_char8_t using u16string = basic_string; using u32string = basic_string; }